Firewalls are obviously a very important and fundamental part of network security. However, that doesn’t make them any less annoying when you’re working in development or just trying to learn the nitty gritty. You may be tempted to just disable the firewall. This will work and you’ll be on your merry way but you’ve learned nothing and when its time to deploy it can be a headache.
When it comes to Microsoft SQL Server, the default instance is easy enough. It operates on port 1433 out-of-the-box. Lets look at how to open this port a couple of different ways.
Using the GUI
To open it up for remote access, simply open Windows Defender Firewall -> Advanced Settings -> Inbound Rules -> New Rule… then follow the wizard:
Select Port and click Next.
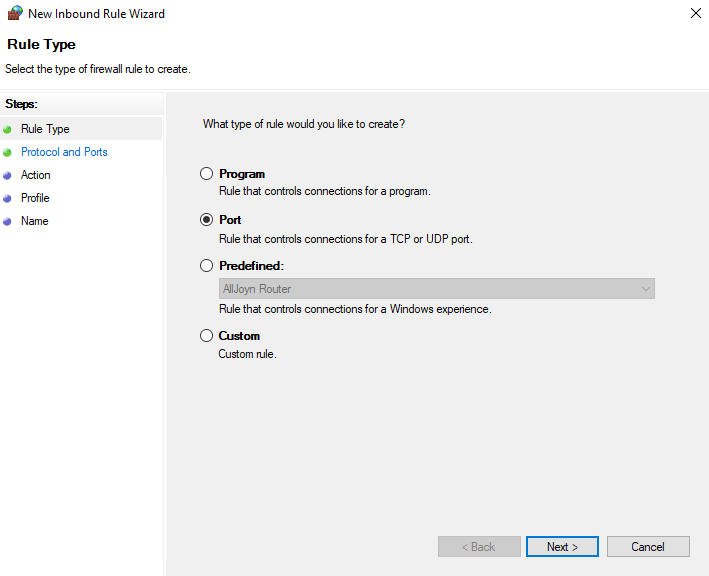
Select TCP and type 1433 into the Specify local ports field
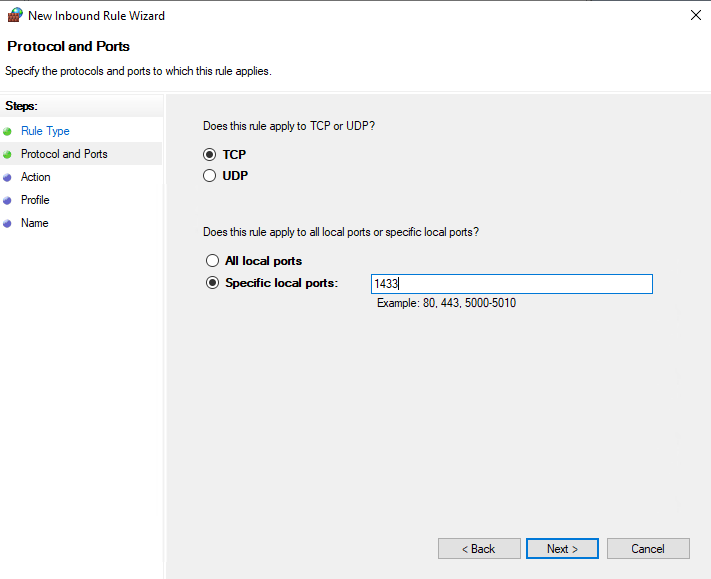
Select Allow the connection and click Next.
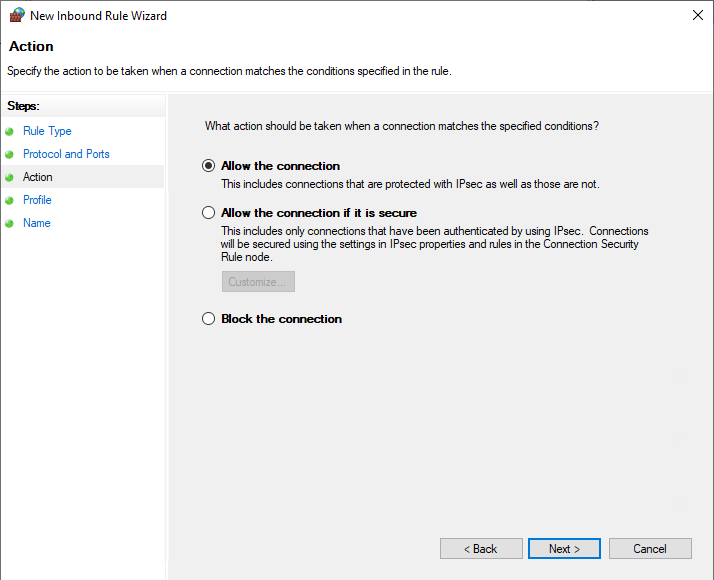
Select the Network Profiles that you want the rules to apply to.
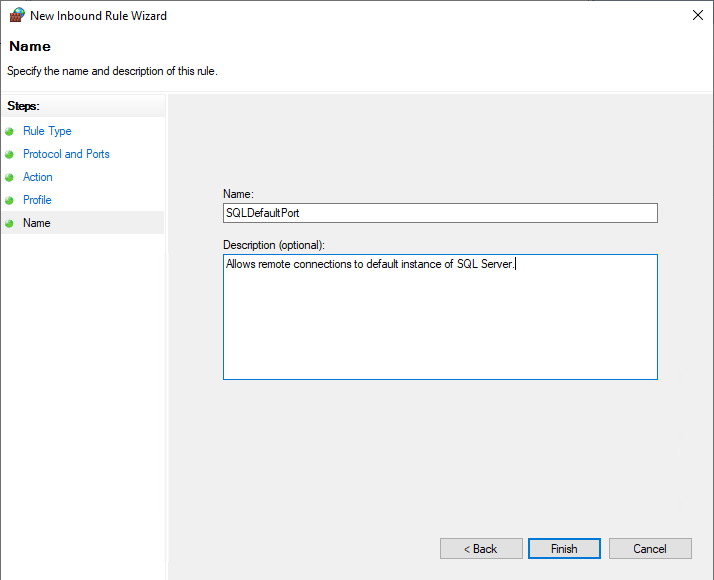
Give the rule a name and description the click Finish.
Using netsh advfirewall
Using the GUI can be time consuming, if you have multiple machines were you need to open ports we can use the netsh utility to administer the firewall through the command line or a batch file.
Running this command will create an inbound rule that opens communication on port 1433 for the domain network profile:
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name = SQLPort dir = in protocol = tcp action = allow localport = 1433 remoteip = localsubnet profile = DOMAINBy default, the typical ports used by SQL Server and associated database engine services are: TCP 1433, 4022, 135, 1434, UDP 1434. The table below explains these ports in greater detail. A named instance uses dynamic ports.
The following table lists the ports that are frequently used by the Database Engine.
| Scenario | Port | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Default instance running over TCP | TCP port 1433 | This is the most common port allowed through the firewall. It applies to routine connections to the default installation of the Database Engine, or a named instance that is the only instance running on the computer. (Named instances have special considerations. See Dynamic Ports later in this article.) |
| Named instances with default port | The TCP port is a dynamic port determined at the time the Database Engine starts. | See the discussion below in the section Dynamic Ports. UDP port 1434 might be required for the SQL Server Browser Service when you are using named instances. |
| Named instances with fixed port | The port number configured by the administrator. | See the discussion below in the section Dynamic Ports. |
| Dedicated Admin Connection | TCP port 1434 for the default instance. Other ports are used for named instances. Check the error log for the port number. | By default, remote connections to the Dedicated Administrator Connection (DAC) are not enabled. To enable remote DAC, use the Surface Area Configuration facet. For more information, see Surface Area Configuration. |
| SQL Server Browser service | UDP port 1434 | The SQL Server Browser service listens for incoming connections to a named instance and provides the client the TCP port number that corresponds to that named instance. Normally the SQL Server Browser service is started whenever named instances of the Database Engine are used. The SQL Server Browser service does not have to be started if the client is configured to connect to the specific port of the named instance. |
| Instance with HTTP endpoint. | Can be specified when an HTTP endpoint is created. The default is TCP port 80 for CLEAR_PORT traffic and 443 for SSL_PORT traffic. | Used for an HTTP connection through a URL. |
| Default instance with HTTPS endpoint | TCP port 443 | Used for an HTTPS connection through a URL. HTTPS is an HTTP connection that uses Transport Layer Security (TLS), previously known as Secure Sockets Layer (SSL). |
| Service Broker | TCP port 4022. | There is no default port for SQL ServerService Broker, but this is the conventional configuration used in Books Online examples. |
| Database Mirroring | Administrator chosen port. | There is no default port for database mirroring however Books Online examples use TCP port 5022 or 7022. It is important to avoid interrupting an in-use mirroring endpoint, especially in high-safety mode with automatic failover. Your firewall configuration must avoid breaking quorum. For more information, see Specify a Server Network Address (Database Mirroring). |
| Replication | Replication connections to SQL Server use the typical regular Database Engine ports (TCP port 1433 for the default instance, etc.) Web synchronization and FTP/UNC access for replication snapshot require additional ports to be opened on the firewall. To transfer initial data and schema from one location to another, replication can use FTP (TCP port 21), or sync over HTTP (TCP port 80) or File Sharing. File sharing uses UDP port 137 and 138, and TCP port 139 if it using NetBIOS. File Sharing uses TCP port 445. | For sync over HTTP, replication uses the IIS endpoint (ports for which are configurable but is port 80 by default), but the IIS process connects to the backend SQL Server through the standard ports (1433 for the default instance. During Web synchronization using FTP, the FTP transfer is between IIS and the SQL Server publisher, not between subscriber and IIS. |
| Transact-SQL debugger | TCP port 135 See Special Considerations for Port 135 The IPsec exception might also be required. | If using Visual Studio, on the Visual Studio host computer, you must also add Devenv.exe to the Exceptions list and open TCP port 135. If using Management Studio, on the Management Studio host computer, you must also add ssms.exe to the Exceptions list and open TCP port 135. |
Service Broker and AlwaysOnAG (mirroring) don’t have defaults. If you need to check what these ports are configured as on an existing system, connect via SSMS or SQLCMD and run the following queries:
AlwaysOn AG (Mirroring):
SELECT name, protocol_desc, port, state_desc
FROM sys.tcp_endpoints
WHERE type_desc = 'DATABASE_MIRRORING'Service Broker:
SELECT name, protocol_desc, port, state_desc
FROM sys.tcp_endpoints
WHERE type_desc = 'SERVICE_BROKER'Batch Script
Below is an example batch script that creates all of the aforementioned firewall rules. Modify the ag_endpnt and sb_endpnt variable at the beginning if your ports are different. Script should be executed from an elevated command prompt or powershell window. Provided for educational purposes only and as always don’t run anything in production that you haven’t tested first.
rem OpenSQLServerPorts.bat
rem Date Modified: 03/26/2021
rem Author: Avery Lane
set "ag_endpnt=5022"
set "sb_endpnt=4022"
rem SQL Default Ports Inbound/Outbound
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name = SQLPort dir = in protocol = tcp action = allow localport = 1433 remoteip = localsubnet profile = DOMAIN
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name = SQLPort dir = out protocol = tcp action = allow localport = 1433 remoteip = localsubnet profile = DOMAIN
rem SQL Dedicated Admin Port Inbound (Default Instance)
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name = SQLPortDedicatedAdmin dir = in protocol = tcp action = allow localport = 1434 remoteip = localsubnet profile = DOMAIN
rem SQL Database mirroring/AlwaysOn AG (Default is 5022)
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name = SQLPortAG dir = in protocol = tcp action = allow localport ="%ag_endpnt%" remoteip = localsubnet profile = DOMAIN
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name = SQLPortAG dir = out protocol = tcp action = allow localport ="%ag_endpnt%" remoteip = localsubnet profile = DOMAIN
rem SQL Browser Service
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name = SQLPortBrowser dir = in protocol = udp action = allow localport = 1434 remoteip = localsubnet profile = DOMAIN
rem Service Broker (Default is 4022)
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name = SQLPortServiceBroker dir = in protocol = tcp action = allow localport ="%sb_endpnt%" remoteip = localsubnet profile = DOMAIN
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name = SQLPortServiceBroker dir = out protocol = tcp action = allow localport = "%sb_endpnt%" remoteip = localsubnet profile = DOMAIN
rem Replication
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name = SQLReplUDP dir = in protocol = udp action = allow localport = 137,138 remoteip = localsubnet profile = DOMAIN
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name = SQLReplTCP dir = in protocol = tcp action = allow localport = 139,445 remoteip = localsubnet profile = DOMAIN
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name = SQLReplUDP dir = out protocol = udp action = allow localport = 137,138 remoteip = localsubnet profile = DOMAIN
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name = SQLReplTCP dir = out protocol = tcp action = allow localport = 139,445 remoteip = localsubnet profile = DOMAIN
Output of netsh advfirewall firewall add rule ?
Usage:
add rule name=<string>
dir=in|out
action=allow|block|bypass
[program=<program path>]
[service=<service short name>|any]
[description=<string>]
[enable=yes|no (default=yes)]
[profile=public|private|domain|any[,...]]
[localip=any|<IPv4 address>|<IPv6 address>|<subnet>|<range>|<list>]
[remoteip=any|localsubnet|dns|dhcp|wins|defaultgateway|
<IPv4 address>|<IPv6 address>|<subnet>|<range>|<list>]
[localport=0-65535|<port range>[,...]|RPC|RPC-EPMap|IPHTTPS|any (default=any)]
[remoteport=0-65535|<port range>[,...]|any (default=any)]
[protocol=0-255|icmpv4|icmpv6|icmpv4:type,code|icmpv6:type,code|
tcp|udp|any (default=any)]
[interfacetype=wireless|lan|ras|any]
[rmtcomputergrp=<SDDL string>]
[rmtusrgrp=<SDDL string>]
[edge=yes|deferapp|deferuser|no (default=no)]
[security=authenticate|authenc|authdynenc|authnoencap|notrequired
(default=notrequired)]
Remarks:
- Add a new inbound or outbound rule to the firewall policy.
- Rule name should be unique and cannot be "all".
- If a remote computer or user group is specified, security must be
authenticate, authenc, authdynenc, or authnoencap.
- Setting security to authdynenc allows systems to dynamically
negotiate the use of encryption for traffic that matches
a given Windows Defender Firewall rule. Encryption is negotiated based on
existing connection security rule properties. This option
enables the ability of a machine to accept the first TCP
or UDP packet of an inbound IPsec connection as long as
it is secured, but not encrypted, using IPsec.
Once the first packet is processed, the server will
re-negotiate the connection and upgrade it so that
all subsequent communications are fully encrypted.
- If action=bypass, the remote computer group must be specified when dir=in.
- If service=any, the rule applies only to services.
- ICMP type or code can be "any".
- Edge can only be specified for inbound rules.
- AuthEnc and authnoencap cannot be used together.
- Authdynenc is valid only when dir=in.
- When authnoencap is set, the security=authenticate option becomes an
optional parameter.