An array is a collection of items stored at contiguous memory locations. The idea is to store multiple items of the same type together. This makes it easier to calculate the position of each element by simply adding an offset to a base value, i.e., the memory location of the first element of the array.
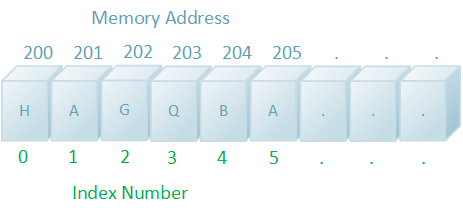
The diagram above demonstrates how each element can be uniquely identified by its index value or by its memory address. Notice that the memory addresses are sequential. This is what is meant by contiguous (touching). This demonstrates how and why order is preserved with arrays.